When a FortiGate is managed by FortiManager, multiple configuration components are tracked to ensure consistency between the device and the management platform. This article explains how FortiManager determines the configuration status of managed devices by comparing the device database, the revision history, and the FortiGate running configuration. It also clarifies the meaning of each configuration status.
FortiManager Device Database and Revision History Database#
Once FortiGate (FGT) is authorized and managed by FortiManager (FMG), a device database is created for that device in FortiManager. You can use the device database to view, configure, and monitor information about managed devices.
FortiManager also maintains a revision history database (or revision history repository) to manage configuration revisions of a device. Using this configuration repository you can view the version history, view configuration details in history, compare revisions, retrieve a revision, or import/download configuration revisions.
To verify each component in FortiManager, follow these steps:
- Device database
Navigate to Device Manager > Device & Groups. Select the desired device and its device database will be displayed. The Dashboard: Summary is first presented:
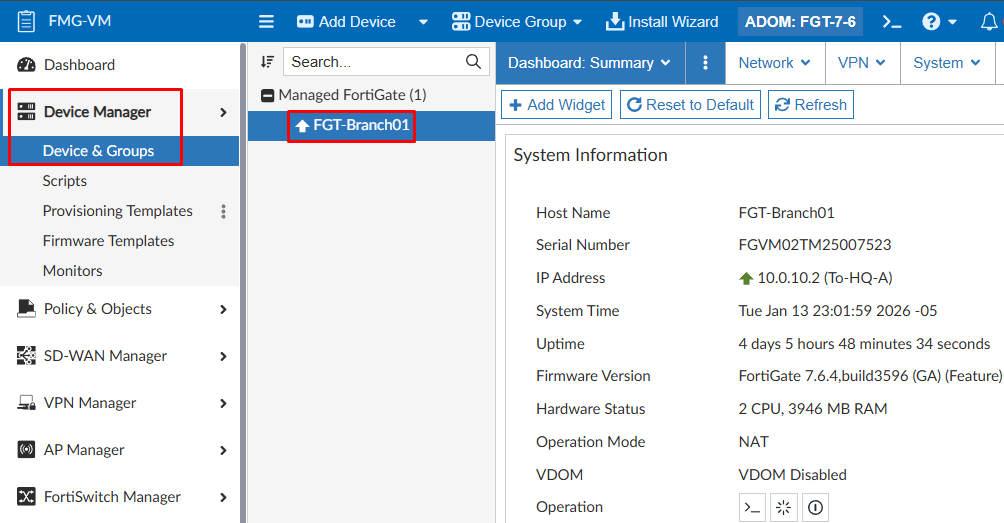
- Revision history database:
From the device database of a specific FortiGate device, under Dashboard: Summary, scroll down to the Configuration and Installation widget:
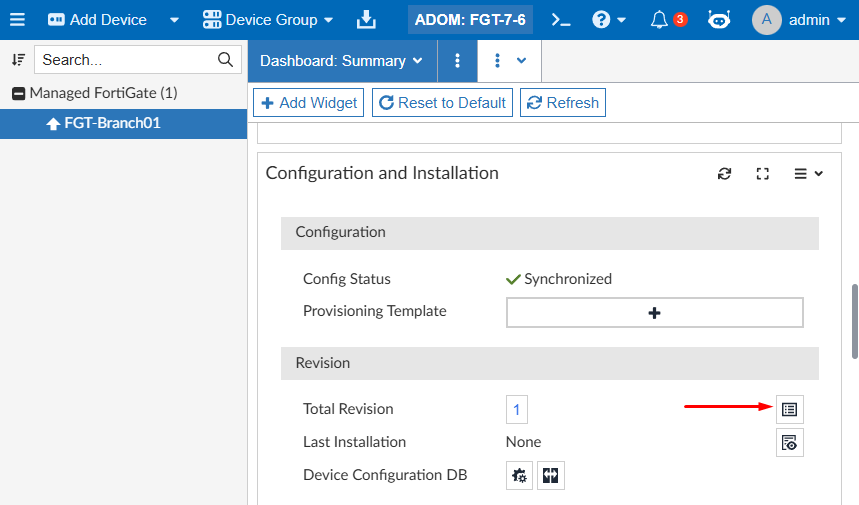
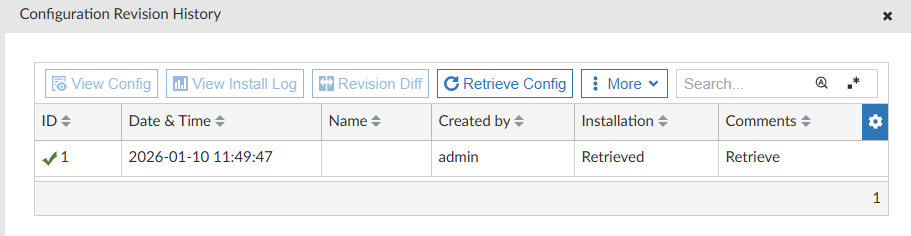
Select the Revision History icon to display all the device configuration revisions:
Managed Device Config Status#
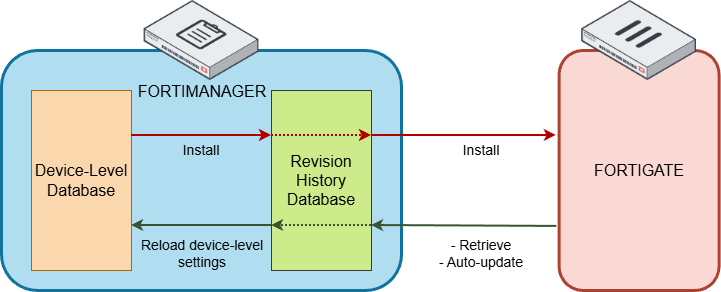
Periodically, FortiManager compares the latest revision history with the FortiGate running configuration to provide a configuration status. Within FortiManager, the latest revision history is also compared to the FortiGate device-level database, to determine if the FortiGate configuration has changed on FortiManager.
The configuration status of a managed device can be verified from Device Manager > Device & Groups. Using a Table view, check under Config Status column:
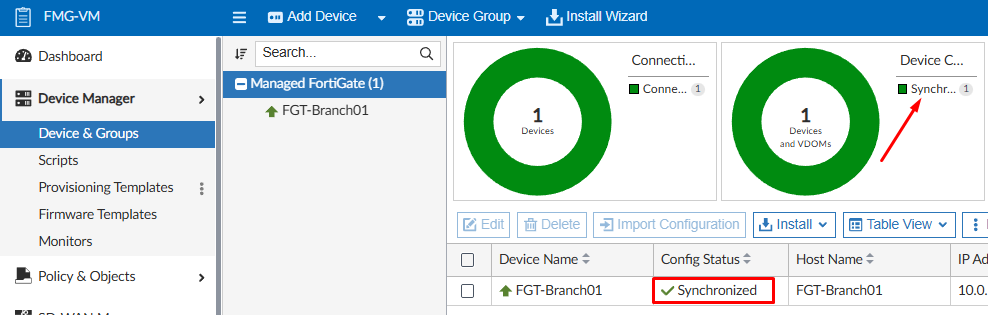
The result of FortiManager latest revision history configuration comparison with both FortiGate running configuration and FortiGate device-level database on FortiManager provides one of the following configuration status:
- Synchronized: the latest revision history configuration entry, whether an install or retrieve, is synced with the managed FortiGate configuration.
- Auto-update: configuration changes made on the managed FortiGate are auto-synced to FortiManager.
- Modified: configuration changes made on FortiManager are not yet synced between FortiManager and managed FortiGate.
- Out of Sync: the latest revision history configuration entry doesn’t match the FortiGate configuration because of local changes made on FortiGate (or a previous partial install failure). A configuration retrieve from FortiManager is recommended.
- Conflict: if one of the following happens: (1) an installation failed; (2) changes were made on FortiManager, while local changes made on FortiGate were not retrieved. You should either retrieve the FortiGate configuration or install changes from FortiManager.
- Unknown: FortiManager is unable to determine the sync status, if one of the following happens: (1) FortiGate not reachable or due to a partial install failure; (2) no revision is generated, like added model device. You should perform a config retrieve from FortiManager.
The different configuration statuses and recommended actions to solve undesired statuses are summarized in the following table:
| Config Status | Device-level DB and Revision History DB | Revision History DB and FortiGate | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
Synchronized - | ✅ | ✅ | Nothing (synced) |
Auto-update - | ✅ | ✅ | Nothing (synced) |
Modified - | ❌ | ✅ | Install changes to FGT |
Out of Sync - | ✅ | ❌ | Retrieve changes from FGT |
Conflict - | ❌ | ❌ | Retrieve changes from FGT + Install changes to FGT |
Unknown - | ❔ | ❔ | Retrieve changes from FGT |
The following diagram depicts how the different configuration components on FortiManager and a managed FortiGate interact with each other:
Device list CLI command#
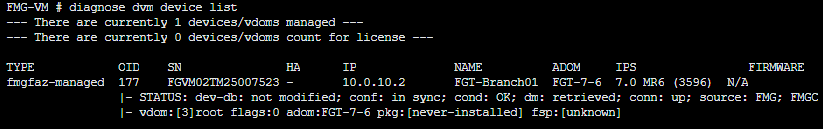
You can use the diagnose dvm device list command to display details of all managed and unregistered devices on FortiManager.
Sample output:
Some important fields of the command output are described below:
OID- Object identifier that uniquely identifies the managed device.HA- FortiGate HA mode (-means FortiGate is working in standalone mode).IP- FortiGate IP address facing to FortiManager.ADOM- ADOM name.FIRMWARE- FortiGate firmware version.dev-db:- device setting status (device-level database), which refers to configuration changes made on FortiManager (modified,not modified).conf:- sync status, which refers to the latest revision historyin syncorout of syncwith the FortiGate device running configuration.cond:- config status, configuration changes need to be installed.conn:- status of the FortiManager connection with the managed device (FGFM tunnel).pkg:- policy package status, which indicates if there is any pending package change on a policy package that has been linked to a device/VDOM (possible values:modified,never-installed, orunknown).